KANGXI 1662 – 1722 Blanc de Chine Porcelain
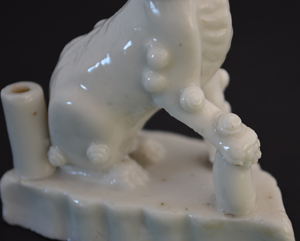
A Pair of Small Blanc de Chine Porcelain Fu Dog Incense Stick Holders, Kangxi Period 1662-1722. The Facing Pair Modelled with Their Mouths Open Exposing Their Fangs, They Sit on Leaf Shaped Bases.
The records of the sale of porcelain from the Dashwood of 1703 include numerous animals, `men on beasts` and 10,800 `square toys` (seals), the 490 `small white dogs` were priced at 1d each.
SOLD
- Condition
- In very good condition, one fang missing a small shallow chip to one base.
- Size
- Length : 7 cm (2 3/4 inches)
- Provenance
- From a Private English Collection of Blanc de Chine Porcelain.
- Stock number
- N/A
- References
- A very similar blanc de chine model from the collection of J.P. Donnelly is illustrated in : Oriental Export Market Porcelain and its Influence on European Wares (Geoffrey A. Godden, Granada, 1979.ISBN 0246110570) page 272, plate 200. Information from Godden`s book ; The records of the Dashwood sale in September 1703, an English Supra-cargo, include 10,800 `square toys` (seals), the other 5,400 `toys` were models of animals, `men on beasts` and the 490 `small white dogs` were priced at 1d each.
Information
Fu Dog, Buddhist Lion, Fo Dog :
When Buddhist priests, or possibly traders, brought stories to China about stone dogs guarding the entry to Indian Buddhist temples, Chinese sculptors modelled statues after native dogs for use outside their temples. The mythic version of the animal, was known as the Dog of Fo, the word Fo being Chinese for Buddha. The Buddhist version of the dog was originally introduced to Han China as the protector of dharma and these dogs have been found in religious art as early as c.200 BC. Gradually they were incorporated as guardians of the Chinese Imperial dharm. However, Chinese sensitivity metamorphosed the dog into a lion, even though lions were not indigenous to China, since this seems more appropriate to the dignity of an emperor when he used the beasts to guard his gates. The mythic dog is sometimes associated with feng shui, and are often called Fu Dogs. Fu means `happiness` in Chinese; however, the term `Fu Dog` and its variant Foo Dog, are not used in Chinese. Instead, they are known as Rui Shi (`auspicious lions`) or simply Shi (lions). There are various styles of imperial guardian lions reflecting influences from different time periods, imperial dynasties, and regions of China. These styles vary in their artistic detail and adornment as well as in the depiction of the lions from fierce to serene.
Blanc de Chine Porcelain :
The porcelain known in the West as Blanc de Chine was produced 300 miles south of the main Chinese kiln complex of Jingdezhen. The term refers to the fine grain white porcelain made at the kilns situated near Dehua in the coastal province of Fujian, these kilns also produced other types of porcelain. A rather freely painted blue and white ware, porcelain with brightly coloured `Swatow` type enamels as well as pieces with a brown iron-rich glaze. However, it is the white Blanc de Chine wares that have made these kilns famous. The quality and colour achieved by the Dehua potters was partly due to the local porcelain-stone, it was unusually pure and was used without kaolin being added. This, combined with a low iron content and other chemical factors within the body, as well as the glaze, enabled the potters to produce superb ivory-white porcelain. White porcelain was made at the Dehua kilns from early times, some books refer to the white porcelain produced during the Yuan period as being Blanc de Chine, but I think it is not really until the latter stages of the Ming dynasty, during the late 16th century, that a porcelain with clearly recognisable Blanc de Chine characteristics was produced. There is a theory that there was a brake in production during a large part of the 18th century. I am highly sceptical of this, it seams likely that Blanc de Chine porcelain was made all the way through, uninterrupted from the Ming dynasty to the present day.