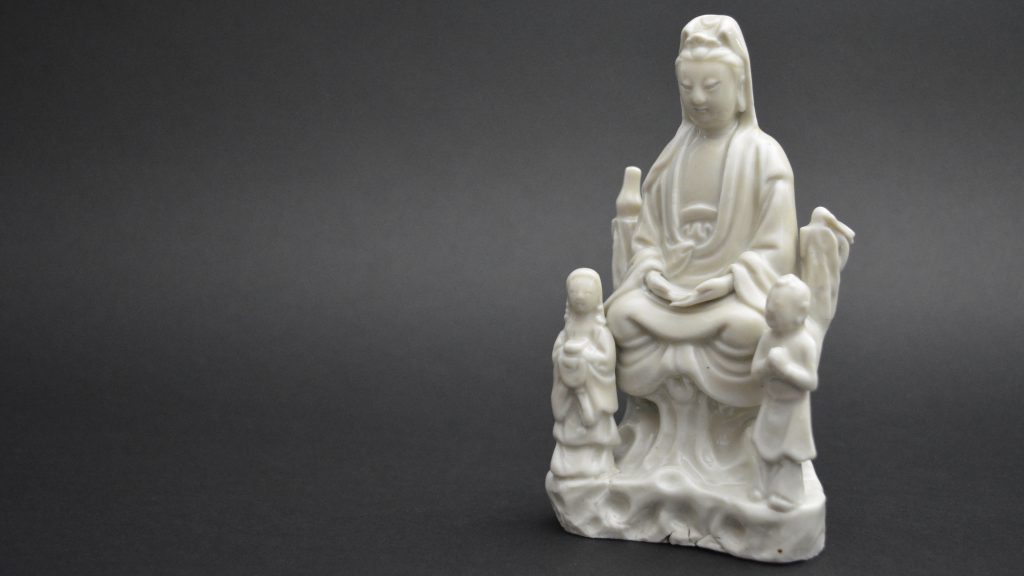
Ming or Qing Blanc de Chine Porcelain Guanyin Group
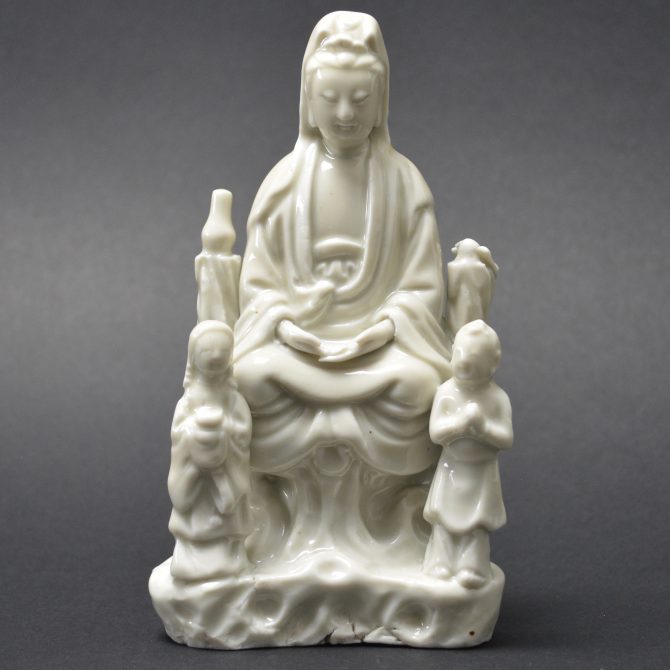
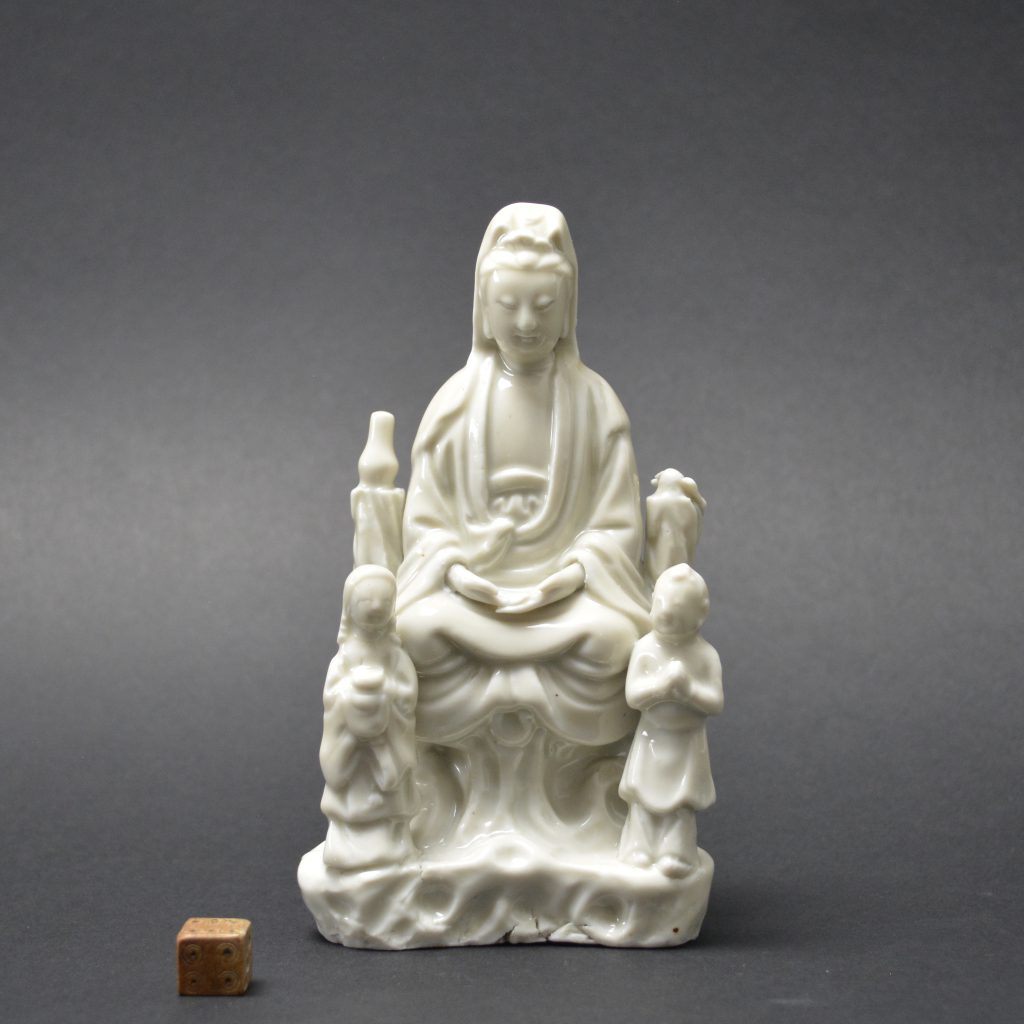
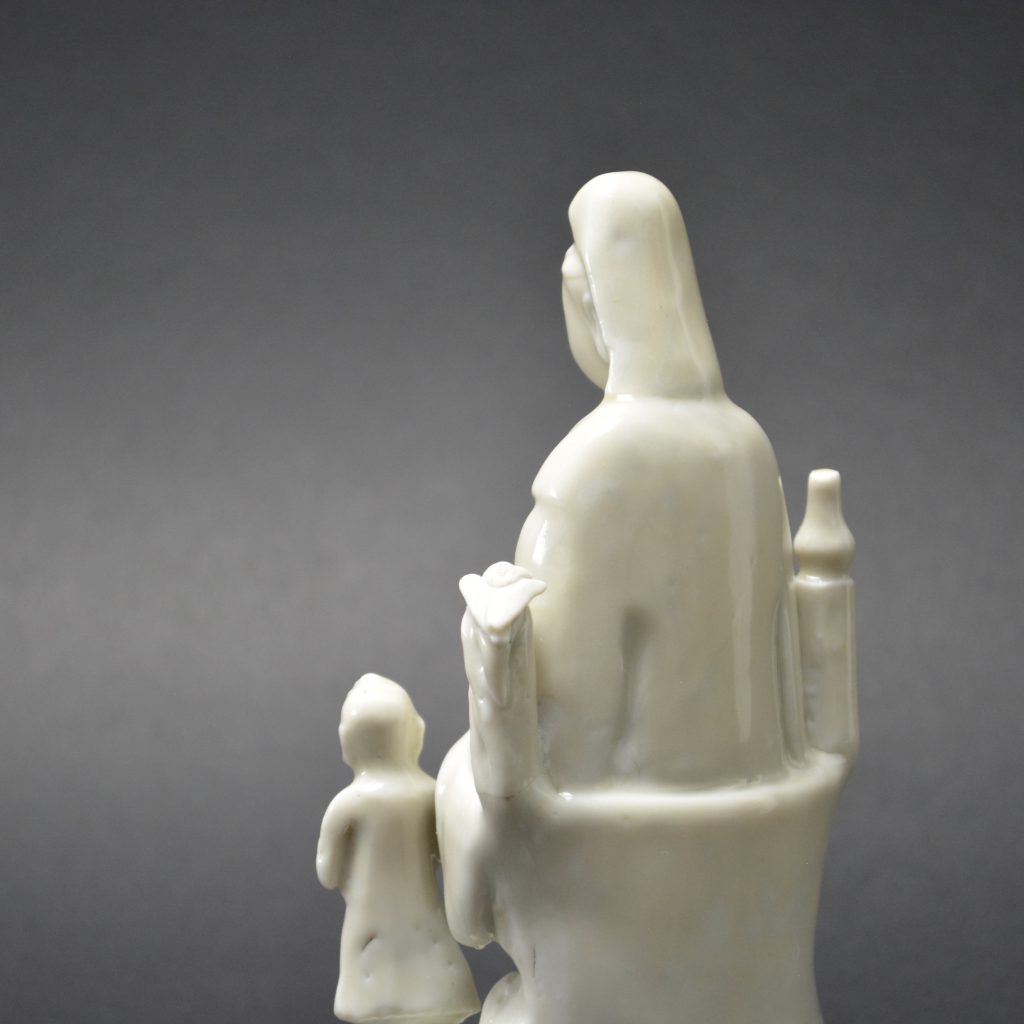
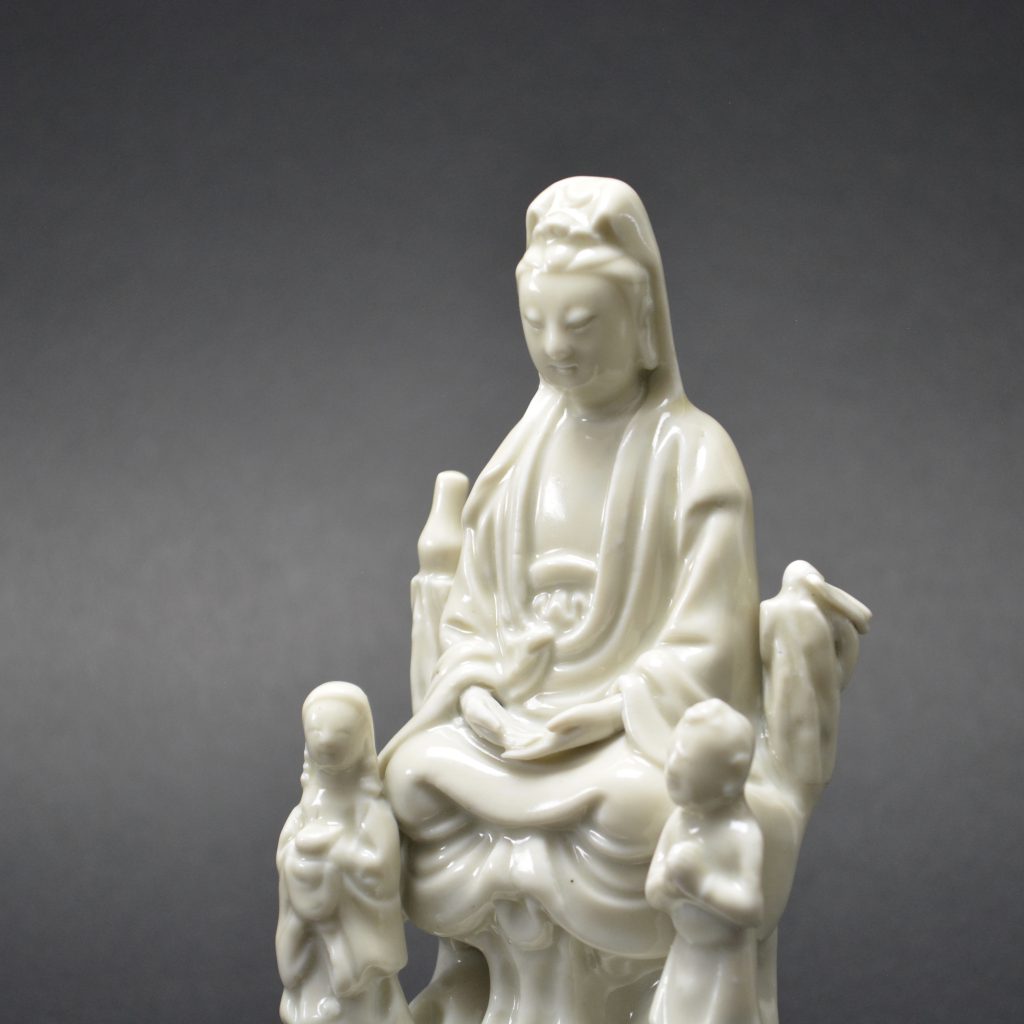
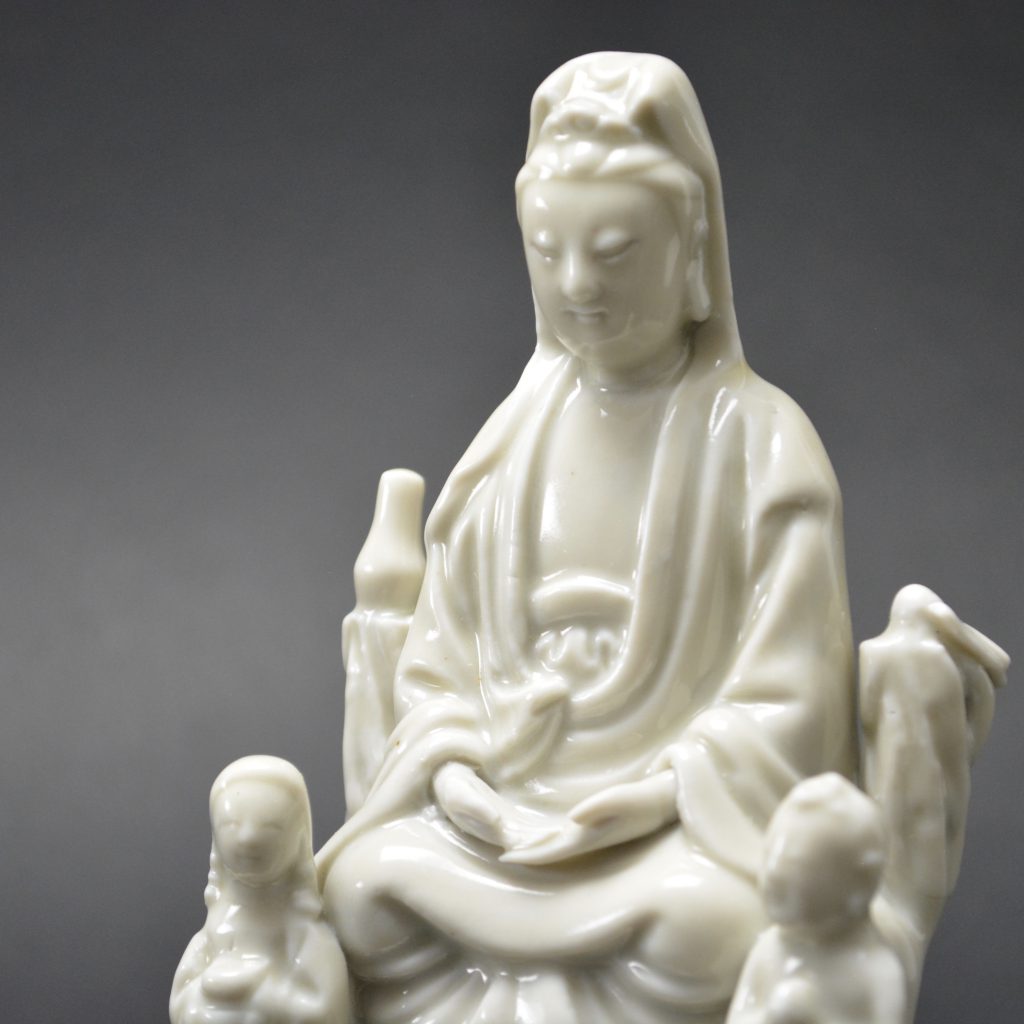
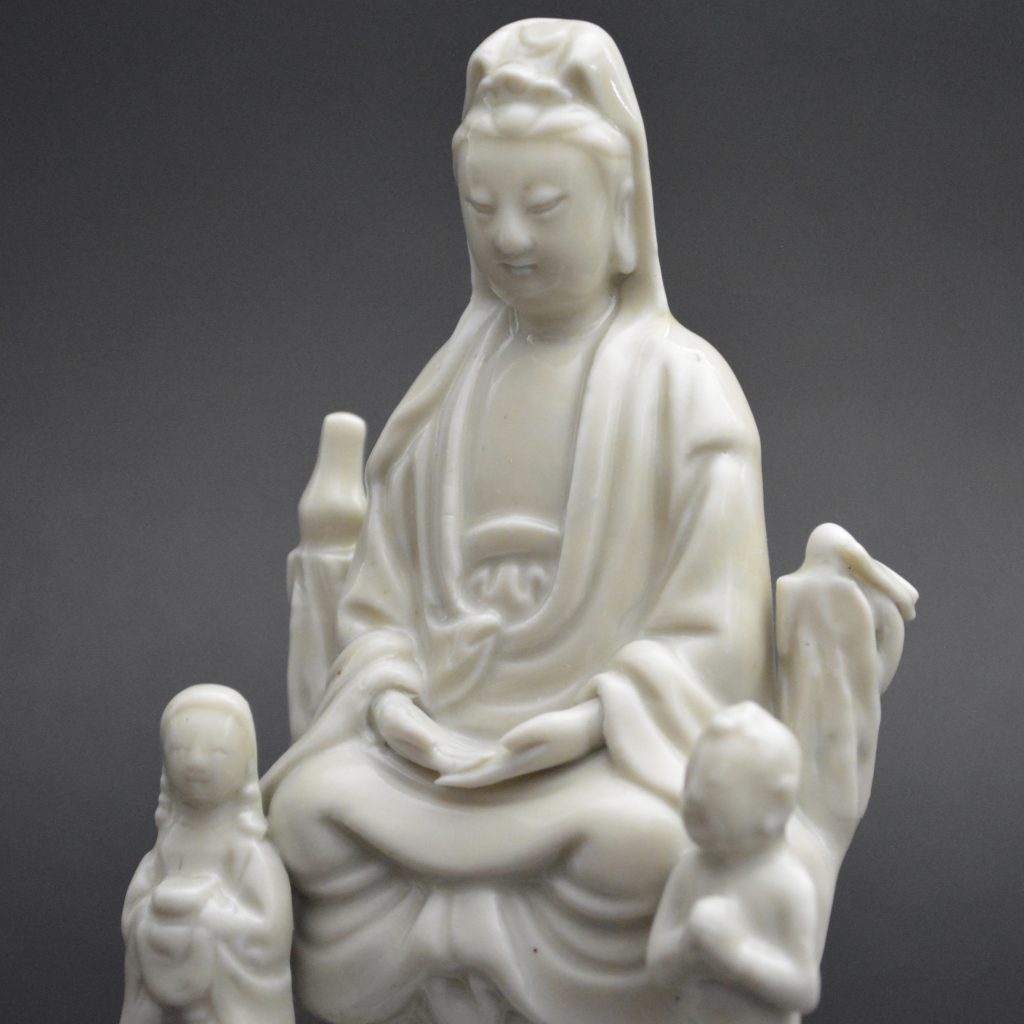
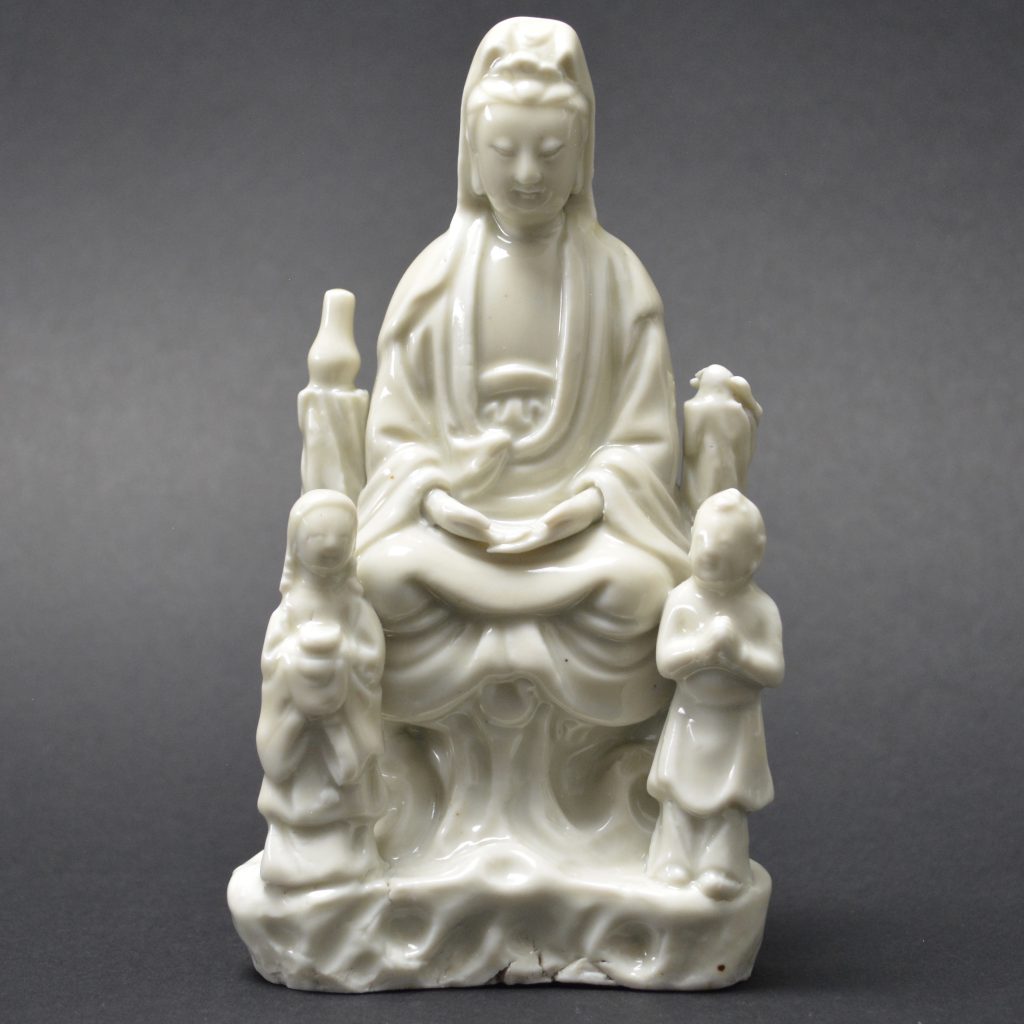
A Ming or Early Qing Blanc de Chine Porcelain Model of Guanyin in Dhyanasana, Late Ming, Chongzhen Period or Shunzhi c.1640 -1660. Dehua Kilns, Fujian Province. This small Blanc de Chine porcelain group includes Guanyin’s acolytes either side of her – Longnu, ‘the Jade Maiden’ and Shancai ‘the Golden Youth’,
SOLD
- Condition
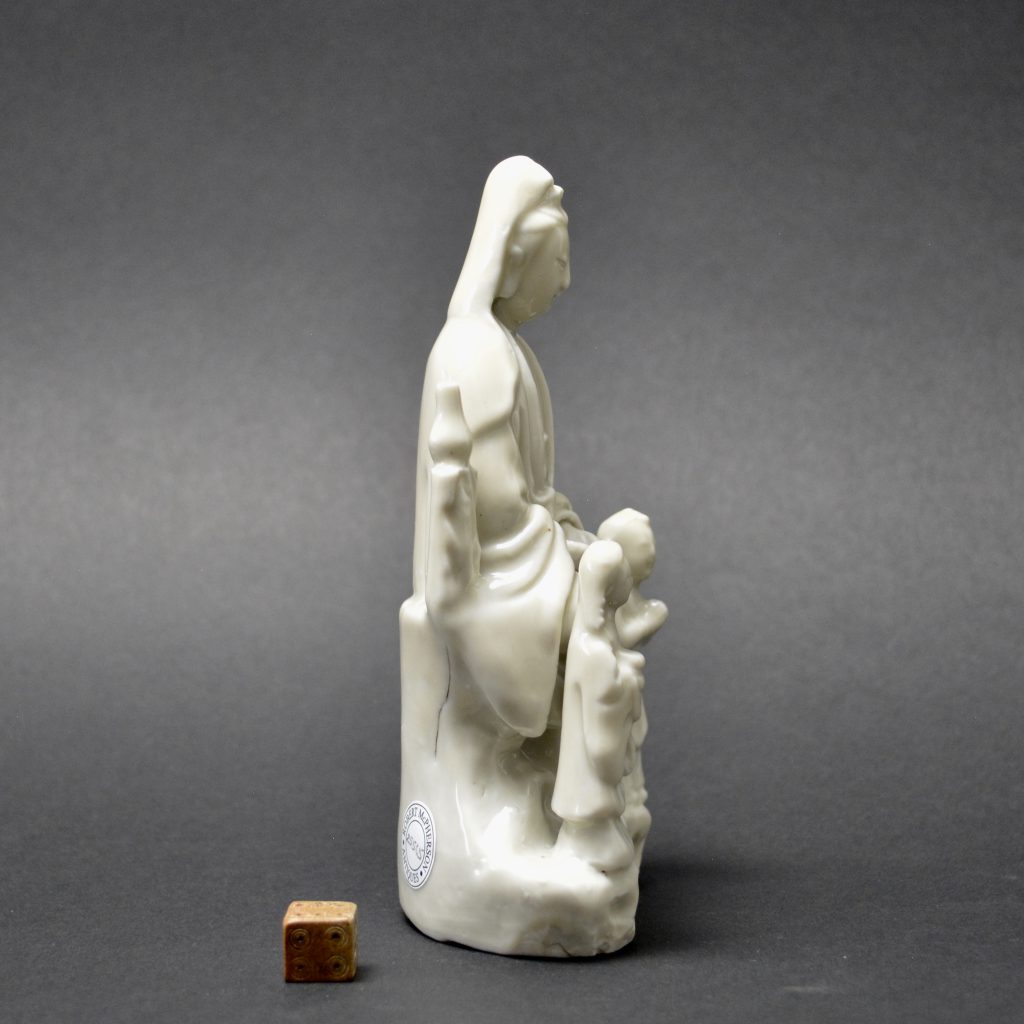
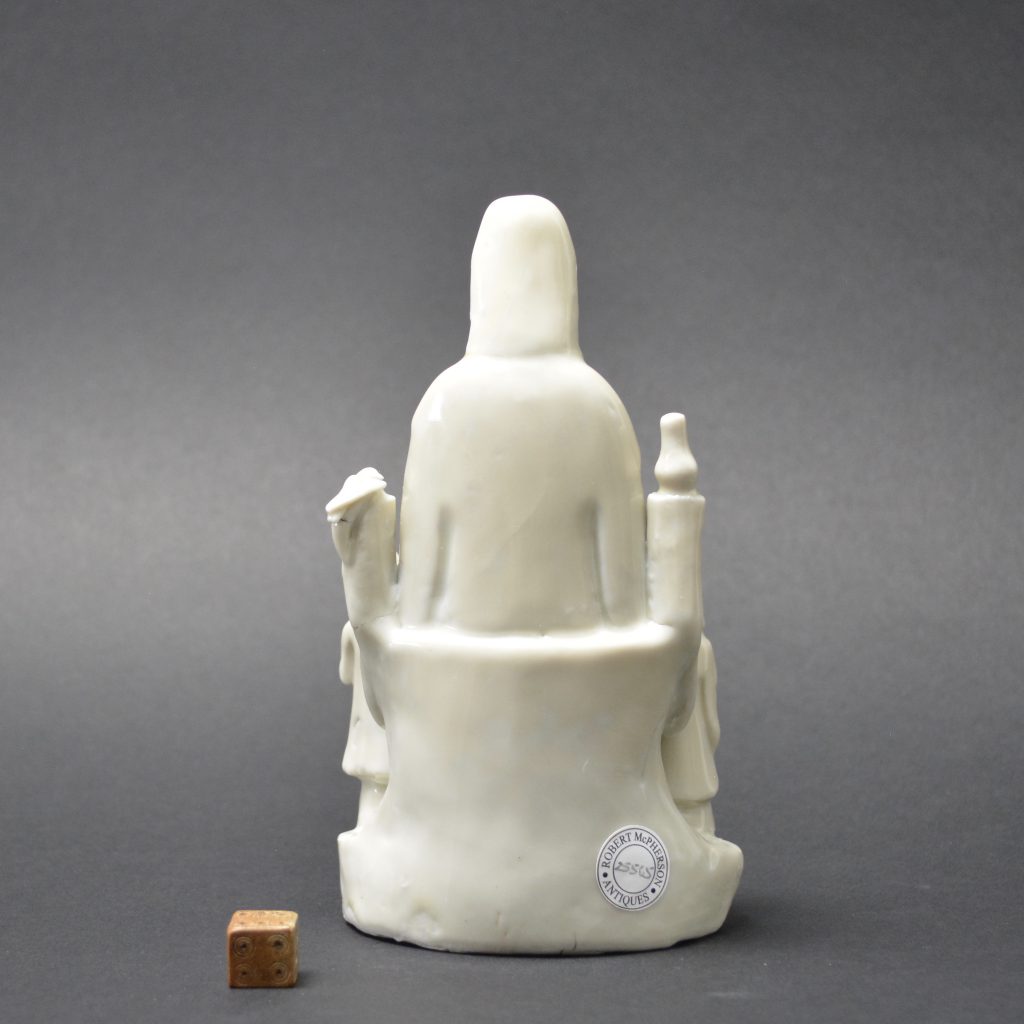
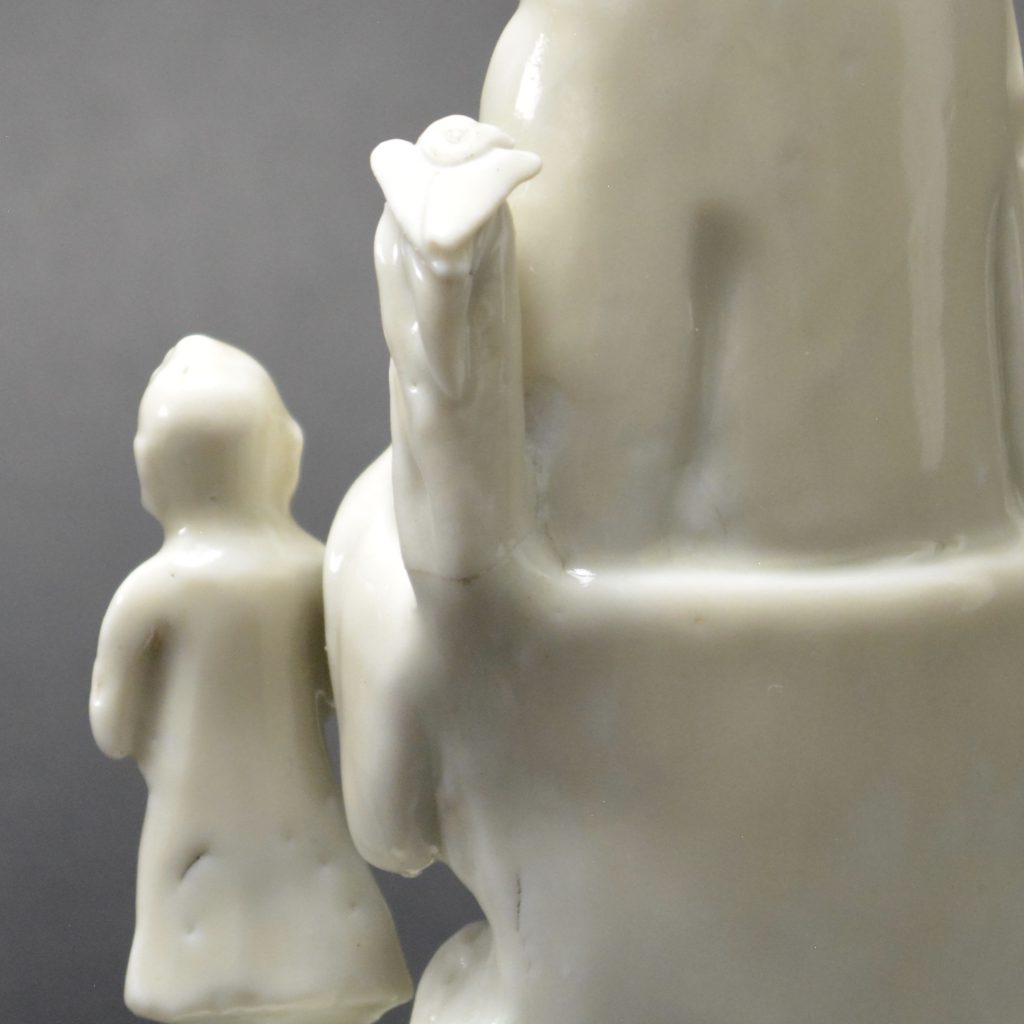
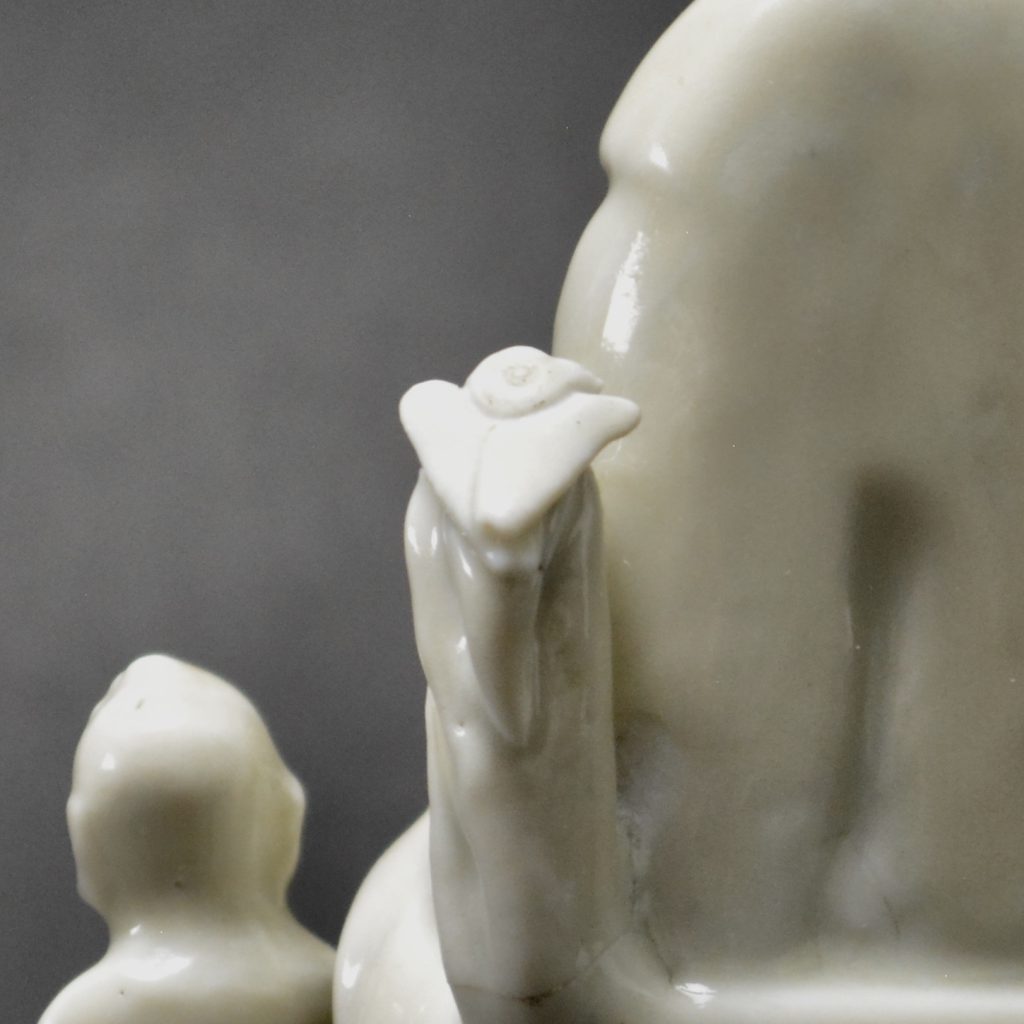
- Damage to the rusticated pillar on Guanyin's left side. This has been broken off and re-stuck. There is a bird on top but this is a cunning adaptation, the original head and neck has been broken off but someone has very cleverly carved a convincing head looking to one side. The carving into the porcelain looks orginal but the head of the bird should be raised. If you touch this repair you can feel that despite it been very smooth, there is no glaze.
- Size
- Height 15cm (6 inches)
- Provenance
- N/A
- Stock number
- 25565a
- References
- This figure is particularly interesting in that it is very similar to the Blanc de Chine Guanyin illustrated in the engraved border of the Dutch map maker Blaeu`s Nieuw Atlas of 1655, see Blanc de Chine, Porcelain From Dehua, A Catalogue of the Hickley Collection, Singapore (Rose Kerr & John Ayers, Art Media Resources Ltd, 2002) page 29, figures 17 and 18, for a close-up of the map and a very similar blanc de chine group. For another similar Blanc de Chine group see our `Sold Items` stock number 18628 and a further related group stock number 20315.
Information
A Similar Guanyin Group Depicted in a Dutch Map of 1655
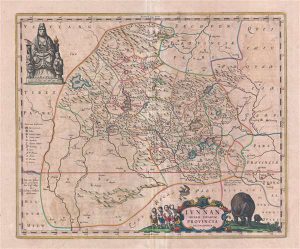
Guanyin
Figures of Guanyin are by far the most common of all Blanc de Chine figures and indeed one of the most common images in Chinese figurative art. Guanyin was the Goddess of mercy, She was especially revered in the area where this figure was produced ; Dehua in Fujian Province. But her origins stem from Tibetan Buddhism, she was originally the patron saint of Tibetan Buddhism `Avalokitesvara`. Guanyin is actually the shorter form of the name Guan shi yin, which means “one who observes the voices of the world.” True to her name, Guanyin listens to and understands the worries that plague man`s existence. Because of her mercy and generosity, Guanyin is the most-loved of China`s divinities. the one people turn to for assistance in their everyday lives. Guanyin is specially venerated by those who are hoping to have children or those who are about to set out for sea. Guanyin is usually portrayed wearing a white cape. In her right hand, she holds a dish that has holy water. On her head is a crown in the style of the Amitabha-buddha. She is shown meditating in a seated position. Guanyin has been given the same qualities as the Virgin Mary of Catholic theology, which is why she is sometimes portrayed holding a child in her arms. While the worship of Guanyin in could be traced historically from India, she is the star of countless legends and folk tales in China. Guanyin`s home on earth was the Putuo mountains, located on an island on China`s eastern coast to the south of Shanghai. In China, Putuo-shan is one of the most sacred places in Buddhism and the temple dedicated to Guanyin on the mountain is one of the most important pilgrimage site for Buddhists and non-Buddhists alike. Guanyin`s birth is celebrated on the 19th day of February, and her enlightenment is celebrated on the 19th of September. On those days, the pilgrims flock to Putuo mountain.
Blanc de Chine Porcelain
The porcelain known in the West as Blanc de Chine was produced 300 miles south of the main Chinese kiln complex of Jingdezhen. The term refers to the fine grain white porcelain made at the kilns situated near Dehua in the coastal province of Fujian, these kilns also produced other types of porcelain. A rather freely painted blue and white ware, porcelain with brightly coloured `Swatow` type enamels as well as pieces with a brown iron-rich glaze. However it is the white blanc de Chine wares that have made these kilns famous. The quality and colour achieved by the Dehua potters was partly due to the local porcelain stone, it was unusually pure and was used without kaolin being added. This, combined with a low iron content and other chemical factors within the body as well as the glaze, enabled the potters to produce superb ivory-white porcelain.
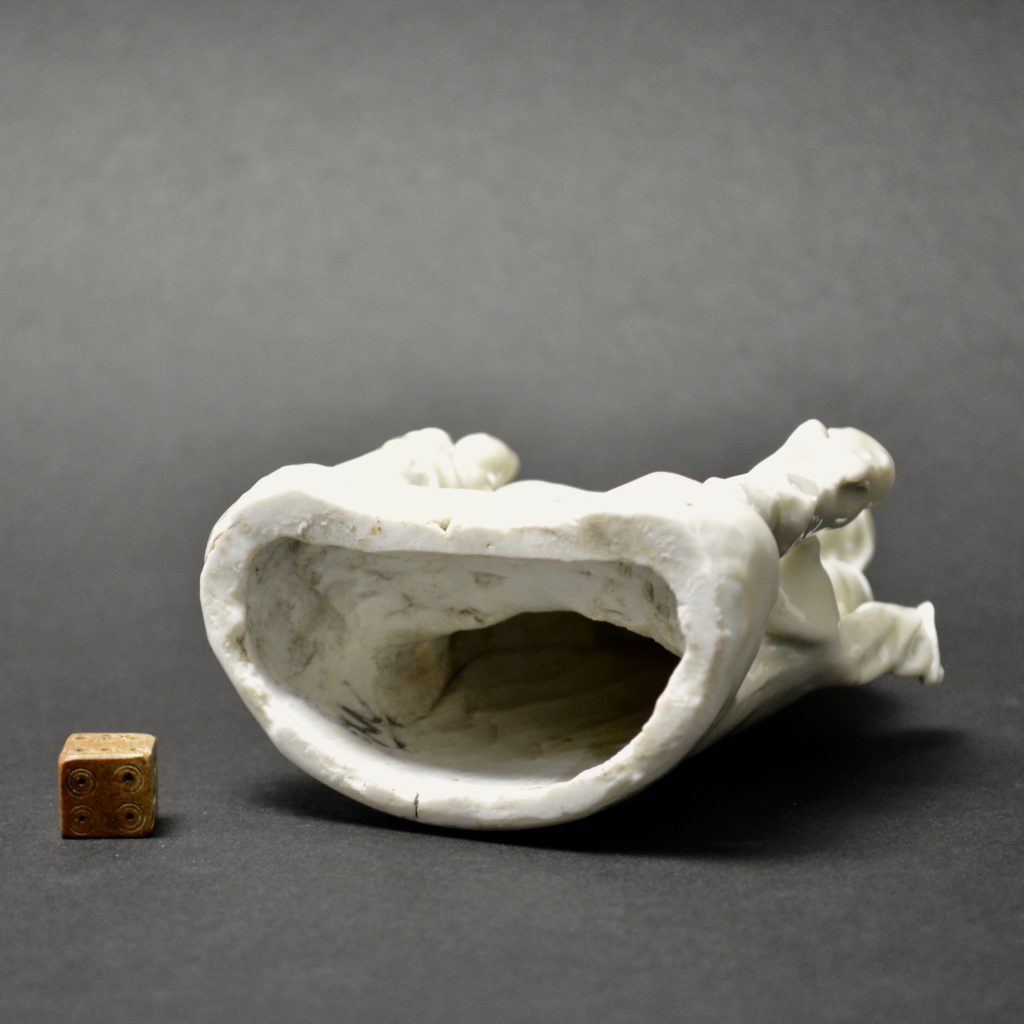
Blanc de Chine Figures of Guanyin
Figures of Guanyin are by far the most common of all Blanc de Chine figures and indeed one of the most common images in Chinese figurative art. Guanyin was the Goddess of mercy, She was especially revered in the area where this figure was produced ; Dehua in Fujian Province. But her origins stem from Tibetan Buddhism, she was originally the patron saint of Tibetan Buddhism `Avalokitesvara`. Blanc de chine figures like the present example were constructed of separate pieces put together, this was a standard technique at the Blanc de Chine kilns in Dehua, it explains the huge variation of seemingly similar objects produced at the kilns. Figures from the Ming dynasty show a far greater degree of hand-modelling, with folds of material, the face, as well as fingers cut by hand. The potting tends to be thicker too, the interior space often shows cutting marks where the excess leather-hard clay was removed. The models of Guanyin from the Kangxi period (1662-1722) appear much more obviously mould-made, the modelling is normally more shallow with less definition and less hand-tooling. The interior wall often shows numerous small finger marks where the potter has pushed the clay into the mould. These figures, especially the taller ones frequently have ridges of porcelain supporting the interior moulded walls, they are pinched to form a ridge which is triangular in cross-section. Blanc de Chine Guanyin Figures : Figures of Guanyin are by far the most common of all Blanc de Chine figures and indeed one of the most common images in Chinese figurative art. Guanyin was the Goddess of mercy, She was especially revered in the area where this figure was produced ; Dehua in Fujian Province. But her origins stem from Tibetan Buddhism, she was originally the patron saint of Tibetan Buddhism `Avalokitesvara`. Blanc de chine figures like the present example were constructed of separate pieces put together, this was a standard technique at the Blanc de Chine kilns in Dehua, it explains the huge variation of seemingly similar objects produced at the kilns. Figures from the Ming dynasty show a far greater degree of hand-modelling, with folds of material, the face, as well as fingers cut by hand. The potting tends to be thicker too, the interior space often shows cutting marks where the excess leather-hard clay was removed. The models of Guanyin from the Kangxi period (1662-1722) appear much more obviously mould-made, the modelling is normally more shallow with less definition and less hand-tooling. The interior wall often shows numerous small finger marks where the potter has pushed the clay into the mould. These figures, especially the taller ones frequently have ridges of porcelain supporting the interior moulded walls, they are pinched to form a ridge which is triangular in cross-section.











